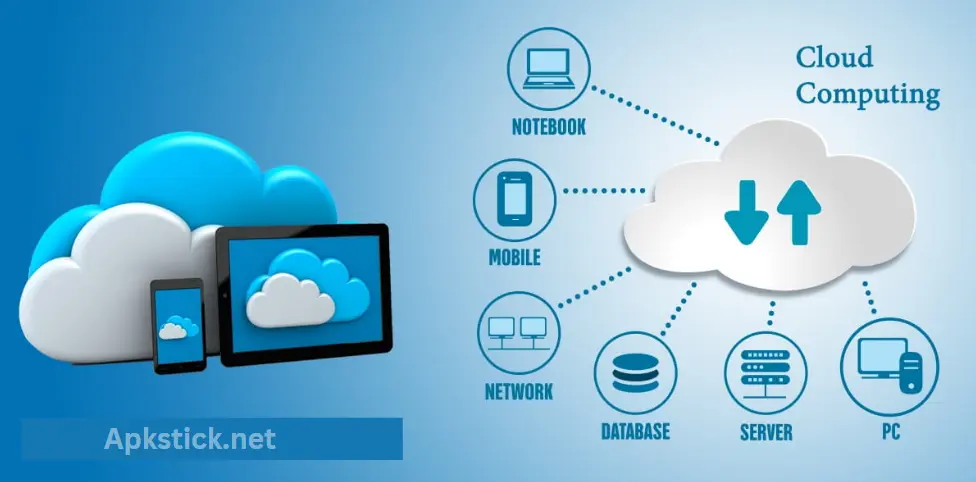
Cloud computing platforms are centralized, on-demand services that provide users with access to computing resources such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics over the internet. Instead of investing in and maintaining physical hardware and infrastructure, users can leverage cloud platforms to access scalable and flexible resources as needed, typically through a pay-as-you-go model. These platforms enable businesses, developers, and individuals to deploy applications, manage data, and run services without the complexities of managing physical IT infrastructure.
Popular cloud computing platforms include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and IBM Cloud. Each offers a wide range of tools and services to support various business needs, from hosting websites to running complex machine learning models. The key benefits of using cloud computing platforms include cost efficiency, scalability, accessibility, and improved collaboration, making them an essential part of modern IT strategies for businesses of all sizes.
What Are Cloud Computing Platforms?
Cloud computing platforms are online services that allow users to access, manage, and store computing resources without needing to own or maintain physical hardware. These platforms create virtual environments where applications can run, data can be stored, and various computing tasks can be performed remotely via the internet.
On-Demand Resources:
Rather than purchasing and maintaining expensive hardware, cloud computing platforms offer computing resources like servers, storage, and databases on demand. You can scale these resources up or down based on your needs, paying only for what you use.
Types of Services:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources, including virtual machines, storage, and networking. Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for developers to build, run, and manage applications without handling the underlying infrastructure. Examples: Google App Engine and Heroku.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. These apps are accessed via a web browser, eliminating the need for installation or maintenance. Examples: Google Workspace and Microsoft Office 365.
Accessibility and Flexibility:
Cloud platforms can be accessed from any device with an internet connection, providing flexibility for remote work, real-time collaboration, and anytime access to your data and applications.
Maintenance and Upgrades:
Cloud providers handle the maintenance, hardware, software updates, and security, relieving your IT team from these responsibilities. This ensures that your systems are always up-to-date with the latest features and improvements.
Why Is Cloud Computing Important?
Cloud computing is important for several reasons, as it revolutionizes how businesses and individuals access and manage technology. Here are the key factors that make cloud computing essential:
1. Cost Efficiency
Cloud computing eliminates the need for businesses to invest in expensive physical infrastructure, such as servers and storage devices. With a pay-as-you-go model, companies only pay for the resources they use, which can significantly reduce upfront and maintenance costs. This makes it easier for small businesses and startups to access high-end technology without substantial financial investments.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud platforms offer unmatched scalability, allowing businesses to quickly increase or decrease their computing resources based on demand. This flexibility helps companies to manage fluctuating workloads, ensuring that they don’t pay for unused resources during off-peak times yet can scale up quickly during periods of growth or increased demand.
3. Accessibility and Collaboration
Cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. This means employees can work remotely, access data, and collaborate in real time, regardless of their location. The ability to share documents, communicate, and work together seamlessly from different parts of the world has made cloud computing a cornerstone for modern collaboration.
4. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Cloud providers take care of infrastructure maintenance, software updates, and security patches. This reduces the burden on internal IT teams, ensuring that the systems remain up-to-date with the latest features, enhancements, and security measures without requiring manual intervention.
5. Disaster Recovery and Data Security
Many cloud providers offer built-in disaster recovery solutions, which means that businesses can quickly restore data in case of a system failure or natural disaster. Additionally, cloud platforms typically have strong security protocols, including encryption and multi-factor authentication, helping protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
6. Increased Innovation and Speed
Cloud computing enables faster deployment of applications and services, helping businesses innovate more quickly. Developers can use cloud-based tools and resources to rapidly build, test, and deploy applications, accelerating time-to-market for new products and services. The availability of cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) on the cloud further fosters innovation.
7. Environmental Benefits
By using shared resources in data centers, cloud computing can lead to more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly operations compared to businesses running their infrastructure. Large cloud providers often invest in sustainable energy sources, reducing the overall carbon footprint.
In summary, cloud computing is essential because it drives cost savings, flexibility, innovation, and operational efficiency while also improving security and disaster recovery. These benefits have made it a fundamental technology for businesses and individuals across industries.
May you also like it:
Top WhatsApp Tracker Apps 2024
Cybersecurity Services – Step By Step Guide
Join TikTok’s Creativity Program Beta: Eligibility & How To Apply
Best Free Movie and Live TV Apps for Android
What are the benefits of a cloud computing platform?
Cloud computing platforms offer a range of benefits that make them an attractive solution for businesses and individuals. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Cost Savings
Cloud computing significantly reduces the need for investing in physical hardware, infrastructure, and maintenance. With a pay-as-you-go or subscription model, businesses only pay for the resources they use, avoiding upfront capital costs and ongoing expenses related to hardware maintenance, electricity, and cooling.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud platforms provide the flexibility to scale resources up or down based on demand. This means businesses can quickly adapt to changing needs, whether it’s handling seasonal spikes in traffic or expanding operations. You don’t need to worry about over-provisioning or under-provisioning, as cloud providers offer dynamic resource allocation.
3. Enhanced Accessibility and Collaboration
Cloud computing enables access to applications and data from any device with an internet connection. This increases mobility and collaboration, allowing employees to work from anywhere, collaborate in real-time, and access business-critical data instantly. This is especially beneficial for remote teams or businesses with global operations.
4. Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Cloud providers handle all infrastructure management, including updates, security patches, and maintenance. This reduces the workload for IT teams, ensuring that systems remain secure, up-to-date, and running smoothly without requiring manual intervention. Providers also often offer high availability, ensuring that applications and data are accessible with minimal downtime.
5. Improved Security
Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security measures like encryption, firewalls, and multi-factor authentication. Cloud platforms often provide better security than most businesses could achieve on their own, with dedicated teams working on constant security updates and compliance with regulations. Additionally, many cloud services include robust data backup and disaster recovery solutions.
6. Disaster Recovery and Data Backup
Cloud computing platforms offer built-in disaster recovery and backup solutions. Data is stored securely off-site, ensuring that businesses can recover quickly in the event of a hardware failure, natural disaster, or cyber attack. This minimizes the risk of data loss and helps businesses maintain continuity in critical situations.
7. Innovation and Agility
Cloud platforms provide access to cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics, which might otherwise be expensive or difficult to implement. These tools enable businesses to innovate faster, gain valuable insights from data, and develop new products or services more quickly. Additionally, the cloud facilitates rapid deployment and testing of applications, leading to faster time-to-market.
8. Environmental Benefits
Cloud computing is often more energy-efficient than traditional on-premise IT infrastructure. Cloud providers operate large-scale, optimized data centers that use energy more efficiently, and many are shifting toward renewable energy sources. By leveraging shared resources, businesses can reduce their carbon footprint compared to maintaining their own servers and data centers.
9. Global Reach
Cloud platforms typically have data centers spread across multiple geographical regions. This global presence allows businesses to offer low-latency services to customers worldwide, improving user experience by providing faster access to applications and data.
10. Focus on Core Business
By offloading IT infrastructure management to cloud providers, businesses can focus more on their core activities and strategic goals rather than dealing with hardware, software updates, or network security. This allows organizations to allocate resources and effort to areas that drive growth and innovation.
11. Improved Performance and Reliability
Cloud providers offer high-performance computing power, with resources such as virtual machines, storage, and databases optimized for speed and reliability. Many cloud services also provide load balancing, ensuring that applications can handle high traffic volumes without degrading performance.
What is serverless computing?
Similar to Platform as a Service (PaaS) solutions, serverless computing allows developers to build applications without the need to manage servers or backend infrastructure. However, unlike PaaS, serverless solutions offer greater scalability, automatically adjusting resources based on demand. While serverless computing simplifies operations by abstracting infrastructure management, it provides developers with less control over the environment compared to PaaS, which allows for more customization and configuration options.
What are the limitations of cloud platforms?
While cloud platforms offer significant benefits, they are accessed over the internet, which introduces the risk of downtime due to outages or performance issues from slow connections. Additionally, businesses utilizing public cloud services have less control over their data and computing resources compared to managing an on-site data center. Security can also be a concern. Although cloud providers implement robust security measures, they operate under a shared responsibility model, which customers often misunderstand. This can lead to security gaps when organizations fail to fully grasp their role in safeguarding the data and assets within their control.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing Platforms
Advantages of Cloud Computing Platforms
- Cost Efficiency
Cloud computing eliminates the need for significant capital investments in hardware and infrastructure. With a pay-as-you-go or subscription model, businesses only pay for the resources they use, reducing overall IT costs and freeing up capital for other areas of the company. - Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud platforms offer the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand. This flexibility ensures businesses can handle traffic spikes or seasonal variations without over-investing in infrastructure. Resources can be quickly adjusted to meet changing business needs. - Accessibility and Collaboration
Cloud services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work, real-time collaboration, and seamless sharing of data and applications. This fosters greater collaboration among teams, regardless of location, and improves productivity. - Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Cloud providers handle all updates, patches, and maintenance for both hardware and software. This reduces the burden on in-house IT teams and ensures that systems remain secure and up-to-date without manual intervention. - Enhanced Security
Leading cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, such as data encryption, firewalls, and multi-factor authentication. Many also offer advanced threat detection and monitoring. These solutions are often more robust than what most organizations could implement on their own. - Disaster Recovery and Backup
Cloud platforms often include built-in backup and disaster recovery solutions, ensuring data is securely stored off-site. In the event of a failure, businesses can quickly restore data and continue operations, minimizing downtime and preventing data loss. - Innovation and Agility
Cloud platforms provide access to cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics. These tools enable businesses to innovate faster, gain deeper insights from data, and stay competitive in the market. - Environmental Benefits
Cloud data centers are typically more energy-efficient than on-premise infrastructure. Large cloud providers often use renewable energy sources and have optimized operations to minimize their environmental impact, allowing businesses to reduce their carbon footprint.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing Platforms
- Downtime and Connectivity Issues
Cloud services depend on internet connectivity, so any network disruption or poor connection can lead to downtime or performance degradation. While cloud providers offer high uptime guarantees, external factors like regional outages or slow internet speeds can still affect accessibility. - Limited Control and Flexibility
With cloud computing, businesses relinquish control over physical infrastructure and rely on the cloud provider for system management and security. This can limit customization options and flexibility in configuring the environment to meet specific needs. - Security and Privacy Concerns
Despite strong security measures, storing sensitive data on third-party cloud platforms can raise concerns about privacy and data protection. In a shared environment, the risk of unauthorized access, breaches, or data leaks exists, especially if customers don’t fully understand the shared responsibility model. - Compliance and Regulatory Issues
Many industries have strict regulations regarding data storage and privacy. Businesses using cloud platforms may face challenges ensuring their data complies with these regulations, especially when data is stored across multiple jurisdictions or in countries with varying data protection laws. - Vendor Lock-in
Moving data and applications between cloud providers can be difficult due to differences in infrastructure, tools, and APIs. This can result in vendor lock-in, where businesses become dependent on a single provider, making it challenging to switch or migrate services without incurring additional costs and complexity. - Hidden Costs
While cloud platforms can be cost-effective, the pricing models can be complex. Charges based on data storage, bandwidth usage, or additional services may lead to unforeseen costs. Without careful monitoring and management, businesses can experience higher-than-expected expenses. - Data Transfer and Latency Issues
Depending on the geographical location of the cloud provider’s data centers, data transfer speeds can be slower, leading to latency issues. For businesses that require real-time processing or have high-performance demands, this could impact performance.
Cloud computing platforms offer substantial benefits in terms of cost savings, scalability, security, and innovation. Still, they also come with risks such as limited control, security concerns, potential downtime, and vendor lock-in. Businesses must carefully weigh these advantages and disadvantages when considering cloud adoption to ensure it aligns with their operational needs and risk tolerance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services (including storage, processing, and software) over the Internet. It allows businesses and individuals to access and use resources without owning or managing physical hardware. These services are hosted on remote servers and can be scaled up or down based on demand.
Is cloud computing secure?
Cloud providers implement strong security measures, including data encryption, firewalls, and multi-factor authentication. However, security is a shared responsibility between the provider and the customer. Businesses must understand their role in securing their data and assets, especially in areas such as access controls and data privacy.
How does cloud computing save costs?
Cloud computing helps reduce the need for capital investment in physical hardware, servers, and data centers. It also eliminates the costs associated with maintaining and upgrading infrastructure. With a pay-as-you-go model, businesses only pay for the resources they use, leading to cost savings in both the short and long term.
What is vendor lock-in in cloud computing?
Vendor lock-in refers to the difficulty or cost of moving data, applications, or services from one cloud provider to another. It occurs when a business becomes reliant on a specific provider’s tools, APIs, or infrastructure, making it challenging to switch to a different vendor without incurring additional costs or facing compatibility issues.
Can cloud computing improve collaboration?
Yes, cloud computing improves collaboration by providing real-time access to shared data, documents, and applications. Teams can work together from different locations, access the latest versions of files, and communicate seamlessly, all of which boost productivity and innovation.
What is cloud scalability?
Cloud scalability refers to a cloud platform’s ability to dynamically adjust resources based on demand. Whether a business needs to handle higher traffic, increase storage capacity, or run more computational tasks, cloud platforms can scale up or down to meet those requirements, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
How does cloud computing help with disaster recovery?
Cloud computing provides built-in disaster recovery solutions by storing data in multiple locations, which ensures business continuity in case of hardware failure, natural disasters, or other disruptions. Cloud services typically offer backup options, allowing organizations to quickly restore data and resume operations with minimal downtime.
Conclusion
Cloud computing platforms have become an essential technology for businesses and individuals, offering a wide range of benefits, including cost efficiency, scalability, accessibility, and security. By leveraging cloud services, organizations can access powerful computing resources without the need for extensive on-site infrastructure, enabling them to focus on innovation, growth, and core business activities. Cloud platforms also facilitate enhanced collaboration, remote work, and disaster recovery, making them invaluable in today’s fast-paced, data-driven world.
However, while cloud computing offers significant advantages, businesses must consider potential drawbacks such as security concerns, limited control over infrastructure, and the complexities of vendor lock-in. Understanding the shared responsibility model, managing costs effectively, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements is crucial to maximizing the benefits of cloud computing.